RADIUS Protocol: A Comprehensive Guide
Key Takeaways
- Triple-A protocol: RADIUS provides centralized Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) for network access control
- Multiple authentication methods: Supports password-based, certificate-based, and token-based authentication for diverse security requirements
- Network-wide compatibility: Works with servers, routers, wireless access points, VPNs, and firewalls across vendors
- RCDevs Radius Bridge integration: OpenOTP Security Suite provides RFC-2865 compliant RADIUS API with multi-factor authentication capabilities
- Enterprise-grade scalability: RCDevs solutions support high availability, load balancing, and extensive integrations including Palo Alto, pfSense, and OpenVPN
- Flexible deployment options: RCDevs Radius Bridge can be deployed on-premise or in cloud environments with comprehensive troubleshooting support
Understanding RADIUS Protocol: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s digital age, security is a top priority for businesses and organizations. One of the most widely used security protocols in the world is RADIUS, which stands for Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service. RADIUS is used to authenticate and authorize access to network resources, including servers, routers, and wireless access points.
In this comprehensive guide, we will take an in-depth look at the RADIUS protocol, how it works, and its benefits. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of the RADIUS protocol and how it can benefit your organization.
What is RADIUS?
RADIUS is a networking protocol that provides centralized authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) for users who connect to and use a network service. It was originally developed by Livingston Enterprises for use with dial-up networks, but it has since become a widely adopted standard for all types of networks.
RADIUS is used by network administrators to manage access to network resources. When a user attempts to connect to a network, the RADIUS server is contacted to verify the user’s credentials. If the credentials are valid, the RADIUS server sends an access approval message to the network access server, which grants access to the user.
How RADIUS Works?
RADIUS works by authenticating users who are trying to access a network resource. It does this by using a username and password, which are passed to the RADIUS server for validation. The RADIUS server then sends a response back to the network access server, which either grants or denies access.
RADIUS also provides authorization and accounting services. Authorization involves determining which resources a user is allowed to access, based on their user profile. Accounting involves tracking the resources that a user has accessed, including the amount of time they have spent on the network and the amount of data they have transmitted.
RADIUS Authentication Methods
RADIUS supports a variety of authentication methods, including:
- Password-based authentication: This is the most common method of authentication, where users enter a username and password to gain access to the network.
- Certificate-based authentication: This method uses digital certificates to authenticate users.
- Token-based authentication: Token-based authentication uses a physical device, such as a smart card or security token, to authenticate users.
Benefits of Using RADIUS
Improved Security
RADIUS provides strong authentication and authorization services, which helps to ensure that only authorized users can access network resources. This helps to prevent unauthorized access and reduce the risk of data breaches.
Centralized Management
RADIUS allows for centralized management of user accounts, which makes it easier to manage access to network resources. This can save time and reduce the risk of errors.
Scalability
RADIUS is highly scalable, which means it can be used to manage access to networks of any size. This makes it an ideal solution for both small and large organizations.
Compatibility
RADIUS is a widely adopted standard, which means it is compatible with a wide range of networking equipment, including servers, routers, and wireless access points.
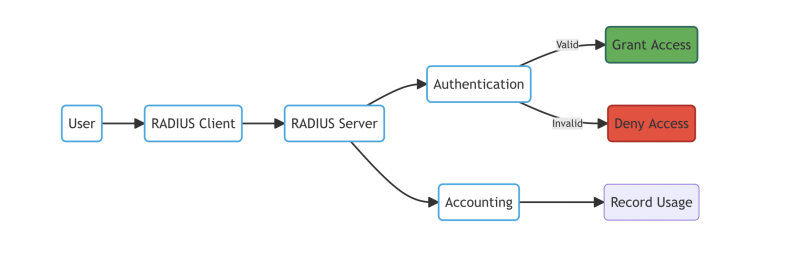
Note: The diagram above shows a high-level overview of how RADIUS works, with the user (A) requesting access to the network through the RADIUS client (B). The RADIUS server (C) then authenticates and authorizes the request (D), granting access (E) or denying access (F). Finally, the RADIUS server records accounting information (G) to track network usage (H).
Modern RADIUS Implementations and Enhanced Security
While the core RADIUS protocol provides robust authentication, authorization, and accounting as described above, modern implementations have evolved to address contemporary security challenges. Today’s RADIUS solutions extend beyond traditional password-based authentication to support advanced security mechanisms including hardware security keys (FIDO2/U2F), certificate-based authentication through EAP-TLS for Enterprise Wi-Fi environments, and multi-factor authentication workflows.
Advanced RADIUS bridges can accommodate both challenge-response authentication methods and concatenated password modes to support various client capabilities. These implementations often include sophisticated policy engines that allow administrators to define granular access rules per client application, user group, or device type. RCDevs’ RADIUS Bridge for example, exemplifies these modern capabilities by offering FIDO2/U2F security key support, EAP-TLS protocols, WebADM Client Policies for granular access control, high availability clustering, comprehensive troubleshooting tools, and seamless integration with Microsoft DirectAccess environments.
FAQ
What Integrations are allowed with RCDevs' Radius Bridge?
What types of non-RADIUS applications can be integrated with RADIUS Bridge?
Can RADIUS Bridge be used for high availability and load balancing?
What authentication protocols does RCDevs' Radius Bridge support?
OpenOTP and WebADM support a range of RADIUS protocols through the OpenOTP Radius Bridge, which provides the RADIUS RFC-2865 (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) API for the OpenOTP Authentication Server. This setup allows for a variety of configurations, including handling of passwords and concatenation, support for Active Directory User Principal Names (UPNs), and the ability to pass additional information such as client ID and user source IP address through specific RADIUS attributes. The OpenOTP Radius Bridge is compatible with numerous integrations and authentications, including but not limited to Palo Alto, NetIQ, pfSense, Swift Alliance Access, OpenVPN, EAP Authentications, and Microsoft Network Policy Server, among others. This extensive support underscores the flexibility and adaptability of the OpenOTP and WebADM platforms to various network and security requirements.
More info : RCDevs' Radius Bridge
Can RCDevs' Radius Bridge be deployed on-premise or in the cloud?
How can I troubleshoot issues with RADIUS Bridge?
- Debug mode with '/opt/radiusd/bin/radiusd debug' for real-time authentication flow analysis
- Built-in 'radtest' tool for testing authentication without VPN clients
- Status checking with 'systemctl status radiusd'
- Network connectivity verification using tcpdump and telnet
- Detailed log analysis in /opt/radiusd/logs/

